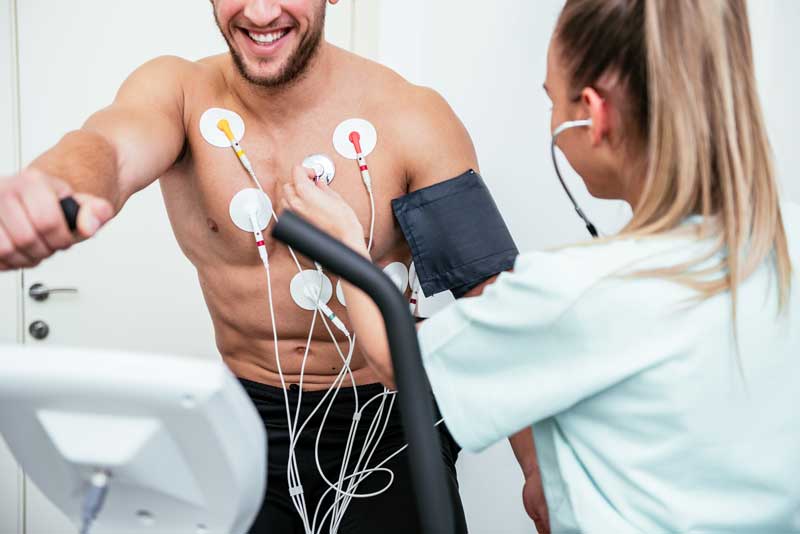
A cardiac stress test, also known as an exercise stress test or treadmill test (TMT stress test), is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the heart's response to physical exertion. During the test, the patient is asked to walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bicycle while their heart rate, blood pressure, and electrocardiogram (ECG) are monitored. The intensity of the exercise is gradually increased to assess the heart's ability to handle stress and detect any abnormalities in blood flow to the heart muscle.
A cardiac stress test is performed for the following reasons:
The test helps evaluate the heart's ability to pump blood effectively during physical activity, providing valuable information about cardiac function and overall cardiovascular health.
Cardiac stress tests are used to detect coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition characterized by narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries. Abnormalities in blood flow during exercise may indicate the presence of CAD.
If a patient experiences symptoms such as chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or palpitations during exertion, a cardiac stress test can help determine the underlying cause and severity of these symptoms.
For patients with known heart conditions or those undergoing cardiac rehabilitation, regular stress testing can help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and assess improvements in cardiovascular fitness over time.
Dr. Rasesh Pothiwala (Divya Heart Care Foundation) All rights reserved. Optimize by SEO Company in Ahmedabad | ARE InfoTech